Have you recently purchased a new electric trolling motor for your boat? Or are you looking to extend the life of your existing motor? Either way, there’s a lot that you need to know about electric trolling motors if you want to get the most out of your purchase.
In this article, we will be talking about the importance of circuit breakers for your electric trolling motor. We will also be discussing the popular types of tolling motor circuit breakers available (a 60 amp circuit breaker for trolling motors, a 50 amp circuit breaker for trolling motors, etc.) and how you can install them. Let’s get started.
Note: most links in this article are Amazon.com Affiliate links, see Affiliate Disclosure, thank you.
Do You Need a Circuit Breaker For Your Electric Trolling Motor?
They may not seem like much, but circuit breakers play a critical role in your electric trolling motor operation. They protect the inner electrical system of the motor and your boat’s wiring. Trolling motors often tend to get overloaded if overheated or jammed with weeds or fishing line.
They are also prone to damage from short circuits. Trolling motor breakers prevent this from happening. If your trolling motor experiences an electrical overload or a short circuit, the trolling motor circuit breaker will be the first thing that receives this surge of electricity. As a result, it will trip or get turned off.
Usually, this surge of electricity results when your propeller or trolling motor experiences additional resistance. This can happen if the propeller is stuck among rocks or entangled in weeds. Since the motor needs to operate at the desired speed, it draws in more power to overcome the resistance.
This increase in electrical current can sometimes be big enough to cause a short circuit. Without the circuit breaker in place, this can cause damage to many critical parts of the motor.
Besides some external factors, the circuit can also experience resistance if:
- A long wire runs to and from the power source
- The wire diameter is inadequate (wrong wire gauge)
- The type of material and number of strands in the wire
- Any corroded or loose connections in the electrical circuit
If you are wondering whether installing a circuit breaker in your trolling motor is optional then, no. The Coast Guard requires a circuit breaker or fuse to protect any ungrounded current-carrying conductor in larger boats.
Trivia: A tripped circuit breaker will prevent the current from passing onward. As a result, the electrical circuit breaks— hence the name ‘circuit breaker.’
Read our article Best Breaker for a 24 Volt Trolling Motor
The Different Types of Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers tend to be categorized according to the capacity of the trolling motor installed in your boat. For example, if your trolling motor draws a maximum current of 60 amperes, then you can install a 60 amp circuit breaker for trolling motors. Some of the distinguishing factors you need to consider before buying a trolling motor circuit breaker for your motor include:
- The motor thrust or model
- The maximum amperage draw for your motor
- The VDC capacity
- The length of the wire extension
Let’s take a look at the different types of circuit breakers available:
50 Amp Circuit Breaker for Trolling Motor
A 50 amp circuit breaker can be used for many different types of trolling motors. There are 4 different types of 50 amp circuit breakers available. These include:
- 50 Amp Circuit Breaker (12 VDC) – This circuit breaker can be used for 30 lb., 40 lb., and 45 lb. trolling motors. The maximum ampere draw for these motors is 30 amperes and 42 amperes.
- 50 Amp Circuit Breaker (24 VDC) – This circuit breaker can be used for a 70 lb. trolling motor. The maximum ampere draw for this motor is 42 amperes.
- 50 Amp Circuit Breaker (36 VDC) – This circuit breaker can be used for a 101 lb. trolling motor. The maximum ampere draw for this motor is 46 amperes.
- 50 Amp Circuit Breaker (48 VDC) – This circuit breaker can be used for an E-Drive motor. The maximum ampere draw for these motors is 40 amperes.
Click here to see a 50 amp circuit breaker on Amazon.com
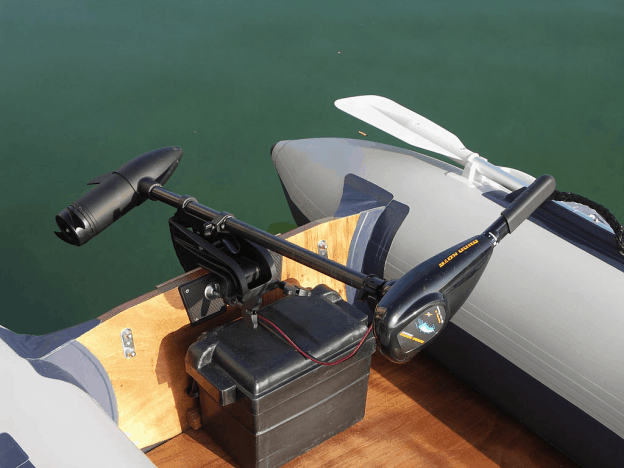

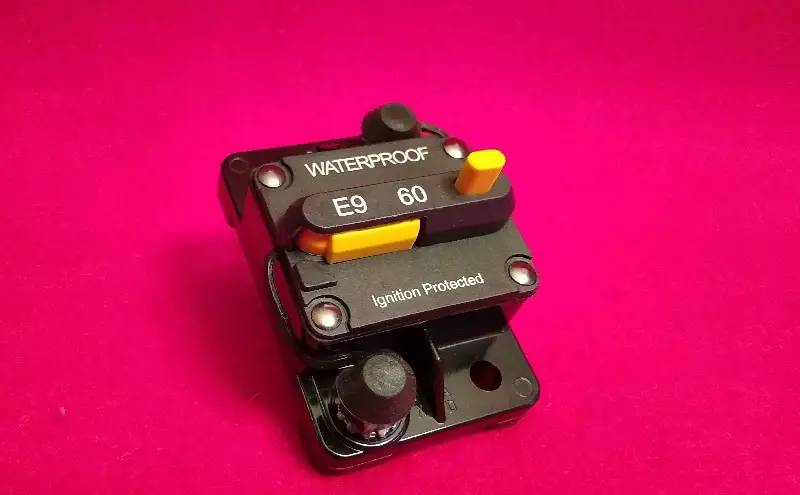
60 Amp Circuit Breaker for Trolling Motor
Like the 50 amp circuit breaker, many different kinds of 60 amp circuit breakers are also available. These include:
- 60 Amp Circuit Breaker (12 VDC) – This circuit breaker can be used for 50 lb. and 55 lb. trolling motors. The maximum amperage draw for these motors is 50 amperes.
- 60 Amp Circuit Breaker (24 VDC) – This circuit breaker can be used for a 80 lb. trolling motor. The maximum ampere draw for this motor is 56 amperes.
- 60 Amp Circuit Breaker (36 VDC) – This circuit breaker can be used for an Engine Mount 101 trolling motor and a 112lb. trolling motor. The maximum ampere draw for these motors is 50 amperes and 52 amperes.
- 2 x 60 Amp Circuit Breaker (24 VDC) – This type involves 2 circuit breakers that can be used for an Engine Mount 160 motor. The maximum ampere draw for this motor is 116 amperes. Together, the circuit breakers provide a capacity to bear a power surge of 120 amperes. This setup is recommended by the manufacturer of this specific motor. Optionally, you can use a Blue Sea Systems MRBF surface and terminal mount fuse block; see the section on fuses below.
Click here to see a 60 amp circuit breaker on Amazon.com
The circuit breakers mentioned above can provide sufficient protection to your trolling motors as long as the following conditions are met:
- The conductor used is appropriately insulated (up to 105°C).
- The maximum number of conductors used is 2
- The voltage drop when the motor is operating at full power should not be more than 5 percent.
Note: The wire extension used for all of these circuit breakers (50 amp and 60 amp breakers) can be between 5 feet to 25 feet long. These differ according to their gauge. Choosing the gauge of the wire that runs from the battery to the motor is very important. This is because the gauge determines whether the wire can handle the power surge or the max amperage draw. If you install a wire extension of the wrong size/gauge, the wire will not be able to withstand the power surge. Instead, it will overheat and cause the insulation to melt. The breaker will be rendered useless, and your motor can get damaged. In extreme cases, you may have to deal with a fire as well.
Click here to check out our article about Wire Gauge Selection.
How to Install a Circuit Breaker For a Trolling Motor
The process of installing a breaker is very straightforward. Typically, you need to add a breaker within 7 inches of the battery on the motor’s positive power cable.
You can hire a marine technician to install a trolling motor circuit breaker. However, if you are looking to do the job yourself, then here’s a set of instructions you can follow:
- Choose a suitable point for mounting the circuit breaker in your boat. It is better if you install the breaker close to the battery/batteries.
- Use the two holes in the base of the breaker to mount the circuit breaker.
- The circuit breaker will have two terminals marked as AUX and BAT. One will be connected to the trolling motor while the other will be connected to the battery.
- Connect the positive power cable of the trolling motor to the terminal that has been labeled “AUX” on the breaker.
- Connect the terminal labeled as “BAT” on the breaker to the positive end of the battery post.
Click here to check out our article on Tips On Installing An Electric Trolling Motor
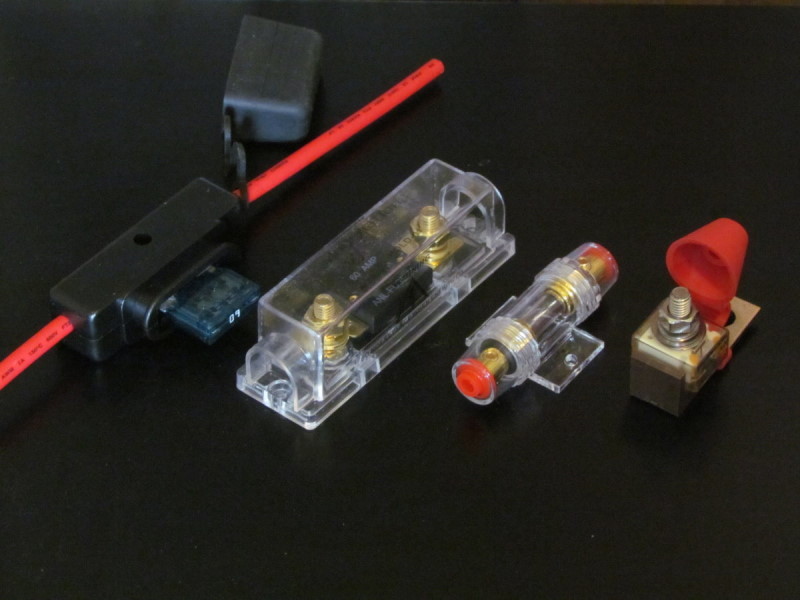
Using a Fuse Instead of a Circuit Breaker
You may receive recommendations for using a fuse instead of a trolling motor breaker for short circuit protection. However, the two are not interchangeable. In the case of a fuse, the extra current flowing through the circuit causes it to heat up.
Once the melting point of the conductor is reached, the fuse blows out, and the circuit is broken. A fuse relies on the accumulation of heat to provide protection. Once it is blown, you will have to replace it with a new fuse.
On the other hand, a trolling motor circuit breaker uses an electromagnet or a bi-metal strip to provide circuit protection. When any extra electric current passes through the circuit, the magnetic force of the strip increases.
This causes a metal lever in the circuit breaker to switch off, and the breaker trips. In the case of a bi-metal strip, the strip bends when it receives extra current. Once again, this causes the metal lever to switch off, and the connection is broken.
Unlike the fuse, the circuit breaker does not get destroyed during this process. When the electrical fault is fixed, you can turn the switch back on and reconnect the circuit. However, repeated breaker tripping can damage the bi-metal strip resulting in a low amperage tripping and eventually complete failure.
Using a fuse instead of a circuit breaker has its advantages. It’s much cheaper, has a high breaking capacity, and is smaller in size. A circuit breaker is comparatively expensive, and some circuit breakers can have a low breaking capacity.
It is also much larger. However, a circuit breaker gives you more convenience and value for money. For starters, you do not need to keep replacing a circuit breaker every time your trolling motor experiences an electrical fault. It can also be reset manually.
A fuse, on the other hand, can provide protection only once. Replacing a fuse can also be very inconvenient. If you plan to use a fuse for your trolling motor, make sure you keep a replacement fuse on the boat as well.
Check out our article In-Line Fuses for 24-Volt Trolling Motor
Additional Tips for Purchasing a Circuit Breaker
To ensure adequate circuit protection, you will also have to keep the following in mind when purchasing a circuit breaker for your trolling motor:
- Make sure you choose a trip-free circuit breaker that can be reset manually
- The circuit breaker must have an adequate ampere interrupting capacity
- The circuit breaker must remain operable after a short circuit or any other electrical fault
- In some cases, you may need to add a fuse before the circuit breaker. This can help increase the ampere interrupting capacity of the circuit breaker.
- Make sure the circuit breaker has been checked for ignition protection. This is done by running a test and supplying an electric current that is 4 times the amount of the breaker’s current rating.
- To prevent short circuits, you can keep the positive terminal(s) of the battery/batteries covered with electrical tape or a protective shield. This can prevent it from coming in contact with metal objects, stray wiring, or anything else that can cause a fault.
- Using a circuit breaker for all wire connections in your boat is advisable.
- When possible, look for breakers for trolling motors or, at minimum, a water-resistant rating like IP65.
Read our article Best Breaker for a 24 Volt Trolling Motor
Click here to read our review of Trolling Motor Batteries
Let’s Sum It Up
Circuit breakers play an essential role in providing circuit protection to your electric trolling motor. Failing to use a circuit breaker can damage your trolling motor and your boat.
It can also put you in danger in case a fire erupts due to an overload or a short circuit. Depending on the trolling motor, you can choose between a 60 amp circuit breaker for trolling motors and a 50 amp circuit breaker for trolling motors.
A few things to keep in mind while buying a circuit breaker include:
- Make sure the circuit breaker suits the model or motor thrust of your trolling motor
- The capacity of the circuit breaker should be according to the maximum amount of current your motor can draw
- Choose a wire extension of appropriate length and diameter. If you use a wire with the wrong gauge, it will overheat in the event of an overload or a short circuit. This will cause the insulation to melt, and the circuit breaker will not be able to do its job.
Read our article Best Breaker for a 24 Volt Trolling Motor
FAQ
Can I use a higher amp breaker than recommended?
You should never use a breaker that is higher than recommended. A breaker is sized to match the limits of your system’s components. These components include things you see like the wiring, the plug, and switches, but they also include things you don’t see, like the trolling motor control board. The proper size breaker will protect your motor from damage and your boat from fire.
What size circuit breaker do I need for my trolling motor?
To choose the right circuit breaker for your trolling motor, you must consider a few factors. The first is the maximum current your trolling motor will draw at any one time, measured in amps. This value can usually be found on a sticker on your motor or in its instruction manual. Next, you need to determine how large of a wire you will be using to connect your trolling motor to the battery bank. Circuit breaker manufacturers have charts that take into account both factors. Tips: Your circuit breaker should be rated 10% above your trolling motor’s max amp draw, and your wire size should be rated 10% above your circuit breaker, accounting for wire length.
What is the difference between a fuse and a circuit breaker?
The main difference between fuses and breaker is that a fuse is a one-time use device, and a breaker can be used multiple times. A fuse is designed to blow as soon as it experiences an overload or short circuit. The broken ends of the fuse stop the current flow, protecting components from damage, like your trolling motor or wiring. A circuit breaker allows for more flexibility because you can turn the breaker on and off as needed. If an overload occurs and your breaker is tripped, after waiting for your breaker to cool, simply turn it back on to resume operating your trolling motor.



[…] To get more information about circuit breakers read our article All You Need to Know About Circuit Breakers for Your Electric Trolling Motor. […]